Understanding the Malaysian Ringgit Currency
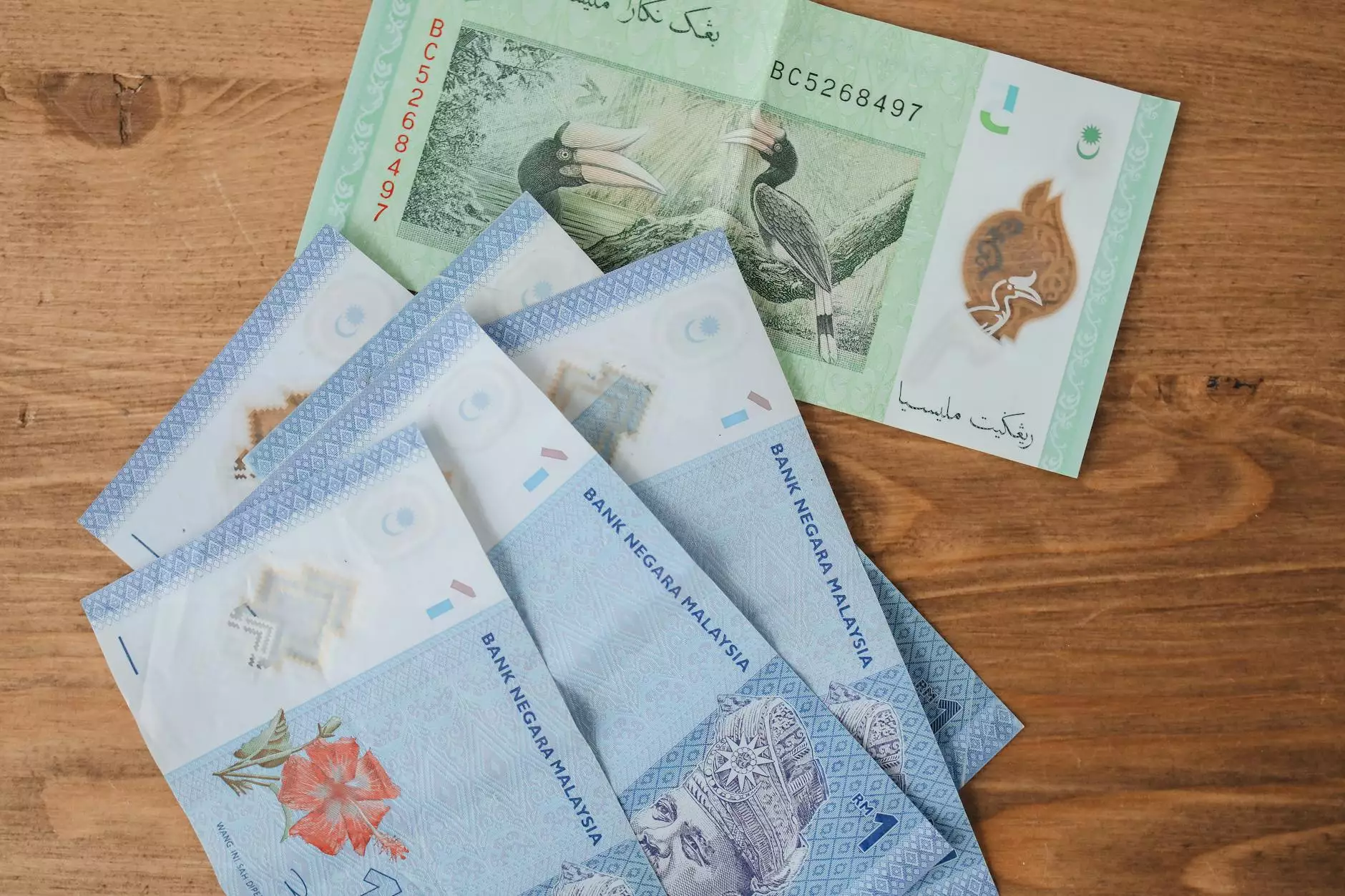

The Malaysian Ringgit currency (MYR) is not just a medium of exchange; it is a symbol of Malaysia’s vibrant economy and its position in the global market. In this article, we will delve deep into the history, features, and significance of this fascinating currency. By understanding the intricacies of the Malaysian Ringgit, businesses and individuals alike can navigate through economic interactions effectively.
The Origin and History of the Malaysian Ringgit
The Malaysian Ringgit currency has a rich history that reflects the changing tides of Malaysia’s economic landscape. Introduced in 1967 to replace the Malayan dollar, the Ringgit was initially pegged to the British pound and later to the US dollar. This transition paved the way for Malaysia to establish its own monetary policy, promoting stability and growth.
The Evolution Over the Years
- 1967: The Ringgit is introduced, solidifying its role as the national currency.
- 1980s to 1990s: The Ringgit sees significant changes as economic policies adapt to globalization.
- 1997 Asian Financial Crisis: The Malaysian government effectively stabilizes the currency, showcasing resilience.
- 2010 onwards: The Ringgit is gradually adopted in international trade, particularly with ASEAN members.
The Features of the Malaysian Ringgit
The Malaysian Ringgit currency is known for its unique features that ensure its integrity and usability in both domestic and international markets.
Physical Characteristics
- Banknotes: The Ringgit is available in several denominations, including RM1, RM5, RM10, RM20, RM50, and RM100. The designs feature iconic Malaysian symbols, ranging from national leaders to significant cultural motifs.
- Coins: Coins come in denominations of 5, 10, 20, and 50 sen, as well as RM1. Their minted designs also reflect Malaysian heritage.
- Security Features: To combat counterfeit money, the Malaysian Ringgit incorporates state-of-the-art security features, such as watermarks, security threads, and color-shifting inks.
Digital Transition
As the world evolves into a digital economy, the Malaysian Ringgit is not left behind. The introduction of electronic payments, online banking, and digital wallets has enhanced the ease of conducting transactions, making it more accessible to the public.
The Role of the Malaysian Ringgit in the Economy
The significance of the Malaysian Ringgit currency extends beyond mere transactions. It plays a crucial role in the economy’s overall health and stability.
Economic Indicator
The strength of the Ringgit often serves as an indicator of Malaysia's economic health. A strong Ringgit can reflect a robust economy, attracting foreign investment and boosting trade opportunities.
Impact on Trade
- Importing Goods: A strong Ringgit means that importing goods becomes cheaper, benefiting consumers but potentially impacting local businesses.
- Exporting Goods: Conversely, a weaker Ringgit may encourage exports, as Malaysian products become more competitively priced on the global stage.
- Tourism: The value of the Ringgit can influence tourism. A favorable exchange rate can attract international tourists seeking to explore the beauty of Malaysia.
Handling Counterfeit Money: Tips for Businesses and Individuals
With the prevalence of counterfeit money and fake documents, it is essential to know how to protect yourself and your business.
Identifying Genuine Currency
One of the most effective methods of combating counterfeit currency is being knowledgeable about the features of genuine Malaysian Ringgit currency. Here are a few tips:
- Feel: Real banknotes have a specific texture. The crispness and weight can help in identifying genuine notes.
- Look: Check for the watermark and security thread. Under bright light, these features should be visible.
- Check: Use a UV light to identify ink patterns and other security features invisible to the naked eye.
Prevention Strategies
Businesses should implement several strategies to protect themselves from counterfeit currency:
- Training Staff: Regularly train employees on how to identify counterfeit notes.
- Use Technology: Invest in counterfeit detection machines which are designed to identify and reject fake banknotes.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest news regarding currency changes and counterfeiting methods.
The Future of the Malaysian Ringgit in a Global Context
As Malaysia continues to integrate more fully into the global economy, the Malaysian Ringgit currency is expected to evolve further. Factors such as technological advancements, changing trade dynamics, and economic policies will all play significant roles in shaping its future.
Global Standing
The Ringgit's conversion into a more internationally recognized currency can enhance Malaysia’s position in foreign markets. By participating more actively in platforms such as the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC), the Ringgit's visibility will increase, improving its stature worldwide.
Innovation in Currency Management
The future also holds potential innovations in currency management, including digital currencies. As financial technologies develop, Malaysia may explore options such as a central bank digital currency (CBDC), which will further integrate the Ringgit within the digital economy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Malaysian Ringgit currency is a pivotal element of Malaysia’s economic identity. Its rich history, unique characteristics, and forecasts for its future emphasize its importance not only within Malaysia but also on a global scale. By understanding the nuances of this currency and implementing effective strategies to handle business transactions, individuals and entrepreneurs can thrive in the dynamic landscape of finance and commerce in Malaysia.
As we move forward, being informed about currency features, recognizing counterfeit money, and embracing digital advancements will be key for a prosperous involvement in Malaysia's vibrant economy.